Lexichem TK
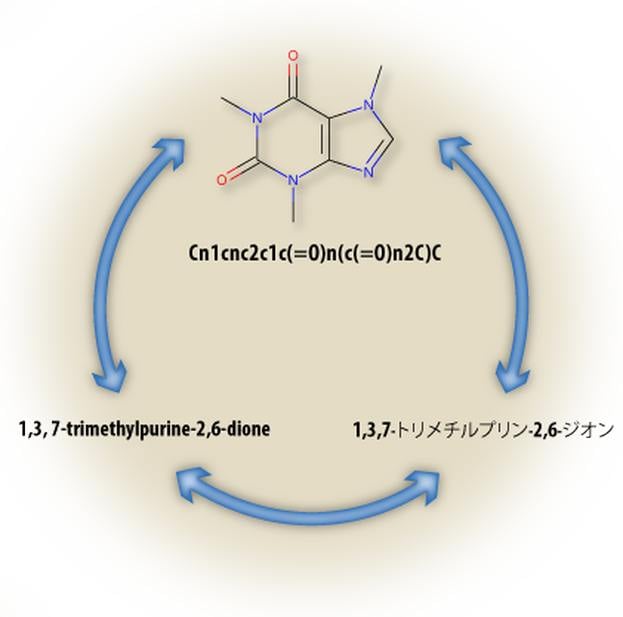
Chemical compound names remain the primary method for conveying molecular structures between chemists and researchers. In research articles, patents, chemical catalogues, government legislation, and textbooks, the use of IUPAC and traditional compound names is universal, despite efforts to introduce more machine-friendly representations such as identifiers and line notations.
The Lexichem TK provides an efficient and highly reliable platform for the interconversion of chemical structures and chemical names [1]. In addition, it also uniquely automates the foreign language translation of chemical nomenclature which is important due to the significant fraction of chemical literature that does not use English nomenclature [2]. This functionality reduces the complications associated with the tasks of filing and analyzing chemical patents, purchasing from compound vendors, and text mining research articles or Web pages.
Support nomenclature
- IUPAC 79 / 93 / 200x
- Chemical Abstracts / CAS
- Traditional
- Systematic
- MDL/Beilstein
- AutoNum
- OpenEye
Supported languages
- English (American, British, International)
- Japanese
- Chinese
- German
- Polish
- Hungarian
- Spanish
- Russian
- Italian
- Swedish
- French
- Slovak
- Romanian
- Danish
- Dutch
- Greek
For more detailed information on Lexichem TK, check out the link below:
Cheminformatics
The Cheminformatics suite of toolkits provides the core foundation upon which all the OpenEye applications and remaining toolkits are built.
- OEChem TK Core chemistry handling and representation as well as molecule file I/O
- OEDepict TK 2D Molecule rendering and depiction
- Grapheme™ TK Advanced molecule rendering and report generation
- GraphSim TK 2D molecular similarity (e.g. fingerprints)
- Lexichem TK name-to-structure, structure-to-name, foreign language translation
- MolProp TK Molecular property calculation and filtering
- Quacpac TK Tautomer enumeration and charge assignment
- MedChem TK Matched molecular pair analysis, fragmentation utilities, and molecular complexity metrics
Modeling
The Modeling suite of toolkits provides the core functionality underlying OpenEye's defining principle that shape & electrostatics are the two fundamental descriptors determining intermolecular interactions. Many of the toolkits in the Modeling suite are directly associated with specific OpenEye applications and can, therefore be used to create new or extend existing functionality associated with those applications.
- OEChem TK Core chemistry handling and representation as well as molecule file I/O
- FastROCS™ TK Real-time shape similarity for virtual screening, lead hopping & shape clustering
- OEDocking TK Molecular docking and scoring
- Omega TK Conformer generation
- Shape TK 3D shape description, optimization, and overlap
- SiteHopper TK Rapid Comparison of Protein Binding Sites
- Spicoli TK Surface generation, manipulation, and interrogation
- Spruce TK Protein preparation and modeling
- Szybki TK General purpose optimization with MMFF94
- Szmap TK Understanding water interactions in a binding site
- Zap TK Calculate Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatic potentials
References
- "New Benchmark for Chemical Nomenclature Software" Edward O. Cannon, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2012, 52 (5),1124-1131.
- "Foreign Language Translation of Chemical Nomenclature by Computer", R. Sayle, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2009, 49 (3), 519-530.
miniCUP Basel 2025
Cadence Announces New Life Sciences Leadership
Expanding Orion’s Capabilities with AI
miniWebinar: Faster, Larger, Smarter: Filling the Funnel for Ultra-Large Scale Virtual Screening
Resources
Glimpse the Future through News, Events, Webinars and more
Event
miniCUP Cambridge 2025
Event
miniCUP Basel 2025


