Permeability Workflow
Calculate permeability coefficient and gain valuable kinetic insight into mechanism of passive membrane permeability, in a fraction of time when compared to other simulation techniques.
The new permeability workflow in the Orion® Small Molecule Discovery Suite helps researchers gain insight into small-molecule drug candidates’ potential chemical absorption and distribution profiles by predicting the speed and manner through which they cross membranes.
The Orion Permeability Floe (guided workflow) can be used early in the drug development process because it leverages a highly parallelizable path-sampling technique to assess permeability at scale. It does not require late-stage molecular synthesis like costly experimental methods, nor does it require prior knowledge of the membrane pathway like thermodynamics-based computational methods.

With the Orion Permeability Floe, researchers get:
Ease of use
Simply input a 2D or 3D structure and be guided through a series of steps that use sophisticated force fields, enhanced sampling methods and MD engines to assess membrane permeability
Valuable mechanistic insight
Predict not only how long it takes for a molecule to cross the membrane, but also what pathways are taken and what happens to a molecule as it traverses the membrane; this may uncover potential structural modifications that could help a drug candidate get across a membrane
Early druggability assessment
Don’t wait until later stages of drug development to assess permeability. Make predictions early on with just 2D structures from a kinetic rate constant. There is no need for a predetermined membrane pathway or lab synthesized molecule, and there’s no need to wait until you have a smaller subset of candidates due to computing constraints
Fast, large-scale calculations
Get results fast by leveraging on-demand AWS compute resources. The Orion Permeability Floe is parallelizable up to thousands of cores and hundreds of GPUs. Current permeability calculations take a few hours and cost a few hundred of dollars per iteration, and the OpenEye team continues to optimize compute times
Reliable science
Trust that the Orion Permeability Floe has been thoroughly tested, showing improved correlation with experimentally predicted permeabilities for a diverse set of molecules, including short-chained alcohols and drug-like molecules, when compared to other computational methods
Flexibility
Have the flexibility to choose different force fields for use with your molecule of interest
Open architecture
Leverage Orion’s Python-based architecture to expand the workflow with third party plug-ins, such as WExplore, Weighted Ensemble (WE)-based string methods, or with a lightweight object-oriented structure analysis library (LOOS).
Permeability Examples
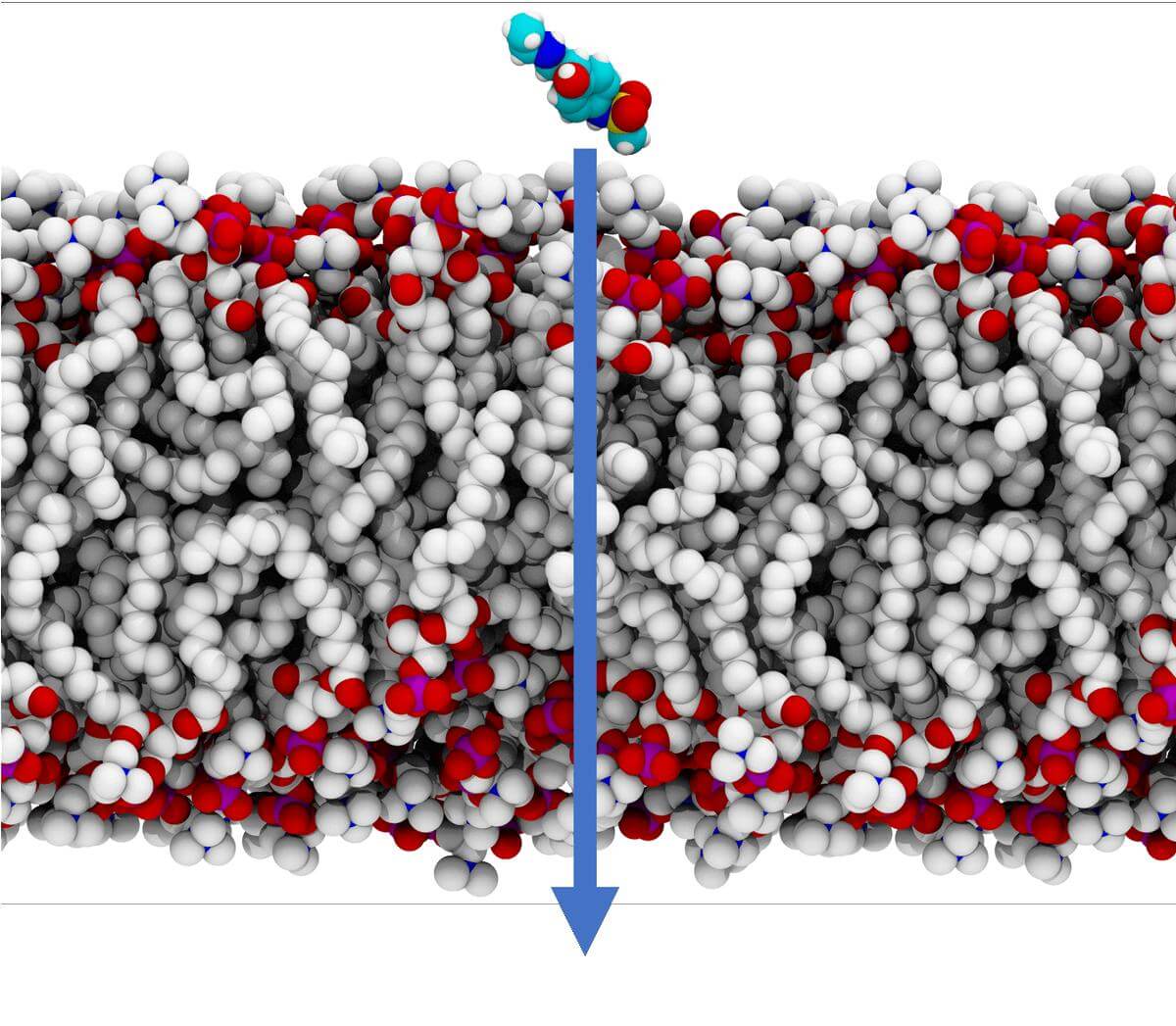
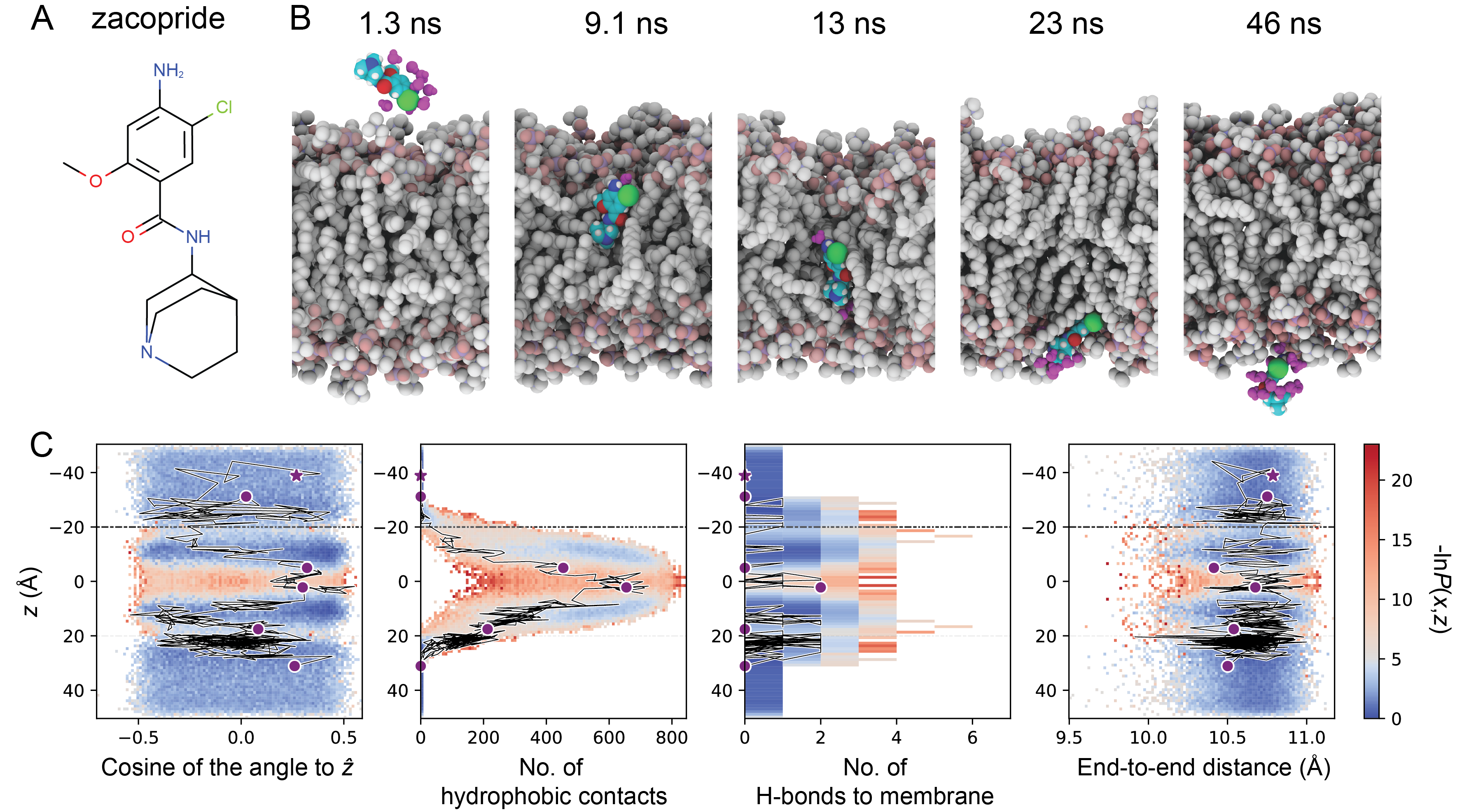
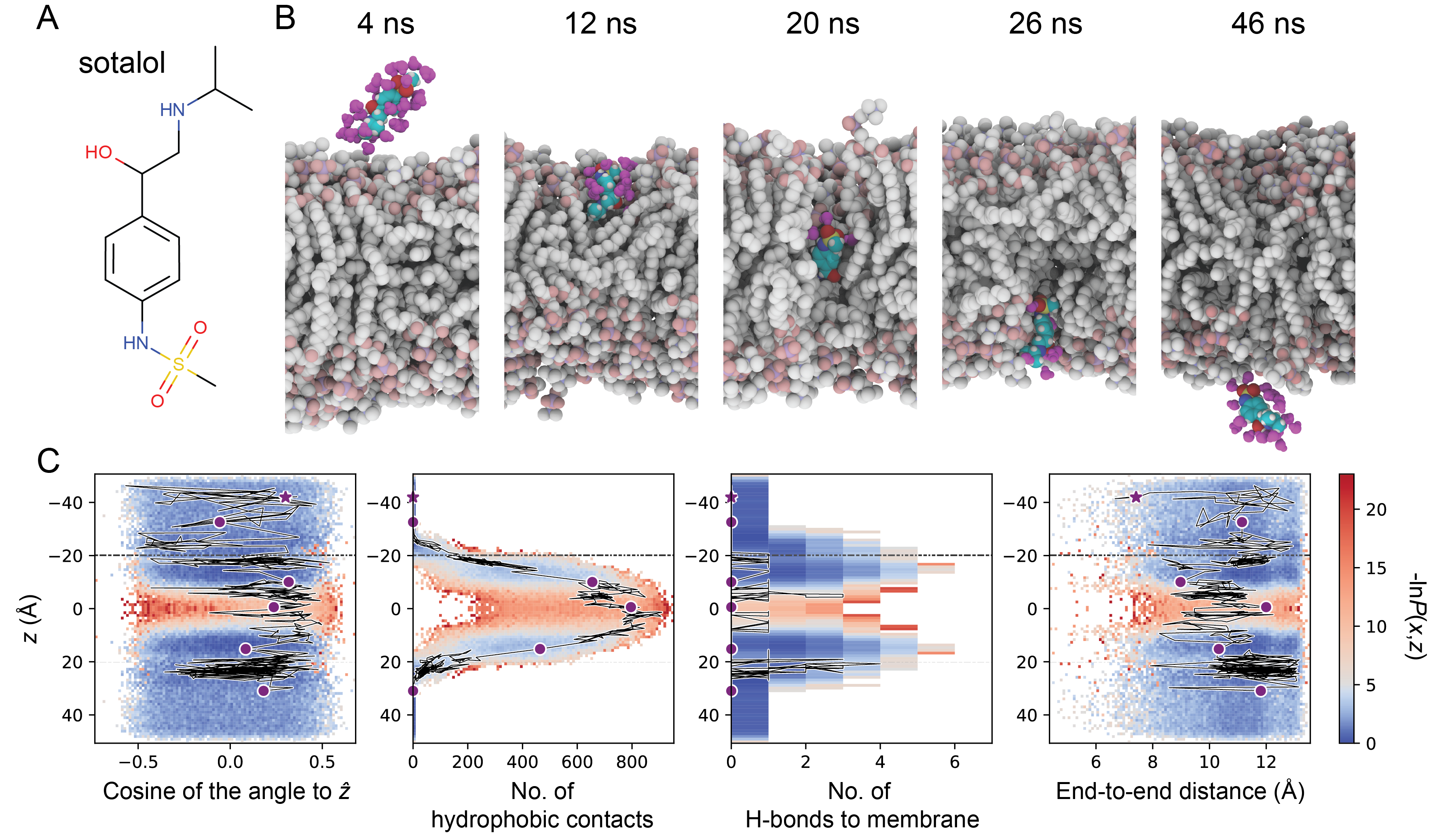
OpenEye's Orion Permeability method can predict how various drugs might cross a membrane. In the examples below, Orion Permeability method predicted various conformational changes for molecules when crossing the membrane. Orion can leverage its cloud-native design to efficiently perform numerous iterations of this calculation to derive a permeability coefficient and identify a dominant pathway, thus providing you with valuable results in a fraction of time when compared to other simulation techniques.
Combining Enhanced Sampling with Cloud Computing
With OpenEye's Permeability method, you can gain kinetic insight into mechanism of passive membrane permeability. Giving you a competitive edge in your drug discovery process... faster.
-
The Orion Permeability Floe walks users through the following main steps:
- Construct 3D molecule from a 2D SMILES string using OEChem
- Solvate the molecule at the correct density using Packmol
- Add the solvated molecule to a pre-equilibrated POPC membrane
- Apply AMBER-based force fields to equilibrate and prepare for permeability analysis, such as Lipid 17 for lipids, PARSLEY for small molecules, or TIP3P for water
- Propagate the dynamics using OpenMM and run weighted-ensemble resampling using the Weighted Ensemble Simulation Toolkit with Parallelization and Analysis (WESTPA) approach
- Output a permeability estimate and permeation pathways
While the early steps of this workflow leverage trusted OpenEye science for system setup, minimization and equilibration, the bulk of new science is a weighted-ensemble approach for assessing permeability. Weighted-ensemble approaches have proven to be very efficient, especially in complex cases, such as when there is a large barrier between the initial and final states.
-
The methodology included in the Orion Permeability Floe is based on the Weighted Ensemble Simulation Toolkit with Parallelization and Analysis (WESTPA) approach, which was developed in Dr. Lillian Chong’s laboratory at the University of Pittsburgh. In addition to seamlessly integrating WESTPA into the workflow, OpenEye refactored the code to leverage AWS parallelization and allow for faster permeability calculations.
-
The Orion Permeability Floe has been validated against a diverse set of molecules, including short-chained alcohols and drug-like molecules. Results showed close correlation with experimentally predicted permeabilities, as well as improved results compared to thermodynamics-based computational methods that can have slow convergence times and poor correlation across different families of small molecules. Validation efforts are ongoing, including studies on more complex molecules with higher degrees of flexibility.
Learn More
To learn more about the Orion Permeability Floe, view the following webinar recordings:
Permeability at Scale: The Weighted Ensemble Method in Orion. (May 2020) Presented by David LeBard, PhD, Senior Scientific Software Developer at OpenEye
How to Exploit Orion as a Scientific Platform? Permeability as a Case Study in Large Scale Floe Development. (Oct 2021) Presented by David LeBard, PhD, Senior Scientific Software Developer at OpenEye
Additional Resources
- Zhang S, Thompson J, Xia J, Bogetti A, York F, Skillman G, Chong L, LeBard D. Mechanistic Insights into Passive Membrane Permeability of Drug-Like Molecules from a Weighted Ensemble of Trajectories. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 8, 1891–1904
Publication Date:April 14, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01540 - Russo JD, Zhang S, Leung JMG, Bogetti AT, Thompson JP, DeGrave AJ, Torrillo PA, Pratt AJ, Wong KF, Xia J, Copperman J, Adelman JL, Zwier MC, LeBard DN, Zuckerman DM, Chong LT. WESTPA 2.0: High-Performance Upgrades for Weighted Ensemble Simulations and Analysis of Longer-Timescale Applications. J Chem Theory Comput. 2022 Feb 8;18(2):638-649. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.1c01154. Epub 2022 Jan 19. PMID: 35043623; PMCID: PMC8825686.
- DeGrave AJ, Ha JH, Loh SN, Chong LT. Large enhancement of response times of a protein conformational switch by computational design. Nat Commun. 2018 Mar 9;9(1):1013. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03228-6. PMID: 29523842; PMCID: PMC5844902.
- Saglam AS, Chong LT. Highly Efficient Computation of the Basal kon using Direct Simulation of Protein-Protein Association with Flexible Molecular Models. J Phys Chem B. 2016 Jan 14;120(1):117-22. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b10747. Epub 2015 Dec 30. PMID: 26673903; PMCID: PMC4716576.
- Zwier MC, Pratt AJ, Adelman JL, Kaus JW, Zuckerman DM, Chong LT. Efficient Atomistic Simulation of Pathways and Calculation of Rate Constants for a Protein-Peptide Binding Process: Application to the MDM2 Protein and an Intrinsically Disordered p53 Peptide. J Phys Chem Lett. 2016 Sep 1;7(17):3440-5. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b01502. Epub 2016 Aug 22. PMID: 27532687; PMCID: PMC5008990.
- Saglam AS, Chong LT. Protein-protein binding pathways and calculations of rate constants using fully-continuous, explicit-solvent simulations. Chem Sci. 2018 Dec 27;10(8):2360-2372. doi: 10.1039/c8sc04811h. PMID: 30881664; PMCID: PMC6385678.
- Zwier MC, Adelman JL, Kaus JW, Pratt AJ, Wong KF, Rego NB, Suárez E, Lettieri S, Wang DW, Grabe M, Zuckerman DM, Chong LT. WESTPA: an interoperable, highly scalable software package for weighted ensemble simulation and analysis. J Chem Theory Comput. 2015 Feb 10;11(2):800-9. doi: 10.1021/ct5010615. PMID: 26392815; PMCID: PMC4573570.
Delivered the Way You Need.
miniCUP Cambridge 2025
Cadence Announces New Life Sciences Leadership
Expanding Orion’s Capabilities with AI
miniWebinar: Faster, Larger, Smarter: Filling the Funnel for Ultra-Large Scale Virtual Screening
Resources
Glimpse the Future through News, Events, Webinars and more
Event
miniCUP Basel 2025
Event
miniCUP Cambridge 2025